Food allergies

By Ayah Wafi
A food allergy is when the body’s immune system reacts when you eat a certain food. Usually, your immune system keeps you healthy and helps protects you from disease by fighting off bacteria, viruses and other dangers using specialized proteins called antibodies. With a food allergy, your immune system overreacts to a certain food and mistakenly identifies the food as a danger. This triggers an allergic reaction where the body produces lots of these antibodies (technically called Immunoglobulin E, or IgE) to 'fight' the food. This antibody production can results in the production of histamines and other regulatory immune chemicals, causing a nasty allergic reaction in the body.
Food allergy reactions occur most often within minutes of eating the trigger food but can take up to 2 hours. Symptoms of a food allergy reactions can affect different parts of the body. Common symptoms of a reaction can include:
- Itchy tongue, mouth throat and ears
- An itchy red rash/hives
- Swelling of the face, eyes, lips, tongue, throat
- Vomiting/Nausea
- Diarrhea
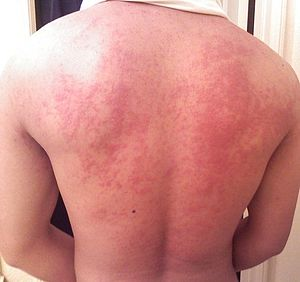
Back rash developing due to food allergy (image from wikimedia commons)
More serious reactions called anaphylaxis can be life threatening and 999 should be dialed as this is an emergency situation. Symptoms of anaphylaxis include:
- Dizziness or feeling faint
- Breath difficulty
- Trouble swallowing
The 14 most common food allergens are:
- Celery
- Cereals containing gluten (such as barley and oats)
- Crustaceans (such as prawns, crabs and lobsters)
- Eggs
- Fish
- Lupin
- Milk
- Molluscs (such as mussels and oysters)
- Mustard
- Peanuts
- Sesame
- Soybeans
- Sulphur dioxide and sulphites
- Tree nuts (such as almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts, brazil nuts, cashews, pecans, pistachios and macadamia nuts).

Food allergies can cause serious reactions in the body (images from TheNounProject and wikimedia commons respectively)
The best way to prevent a food allergy reaction is to identify what food is causing the allergy and avoid it. If a food allergen is eaten then antihistamines work well for mild and moderate reactions. In more severe reactions such as anaphylaxis an auto-adrenaline injection such as an EpiPen is an effective treatment. (Please refer to NHS guidelines for health advice https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/anaphylaxis/)

Injectable EpiPen
Activity:
- Sarah is allergic to milk
- Hannah is allergic tree nuts, peanuts, and sesame seeds ·
- Kabir is allergic to eggs
- Jamal is allergic to wheat
Can you identify the foods that are not safe for Jamal, Kabir, Hannah and Sarah to eat from this list below?
You can do this by searching the labels of these foods online to see what allergens they contain or may contain and if they are safe for Kabir, Hannah, Jamal and Sarah.
Take note that labels which say made in the same factory as an allergen could still pose a risk to allergic consumers due to cross contamination.
| Greek Yogurt | |
| Mayonnaise | Jamal |
| Peanut Butter | |
| Heinz Baked Beans | |
| M&Ms | Kabir |
| Skittles | |
| Hummus | |
| Meringue | Sarah |
| Worcestershire Sauce | |
| Seeded bagels from your local supermarket | |
| Licorice | Hannah |
| Bourbon Biscuits |
More resources on food allergy:
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/clips/zpdy6fr
https://www.food.gov.uk/sites/default/files/media/document/top-allergy-types.pdf https://www.allergyuk.org
https://www.anaphylaxis.org.uk